
|
Atomic absorption spectrometry (AAS)
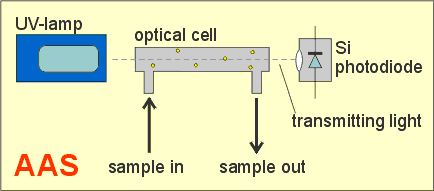 |
Mercury vapors absorb
UV-light at wavelength 253.7 nm. This method for mercury determination
is called as a "Cold Vapor Atomic
Absorption Spectrometry" (CVAAS) |
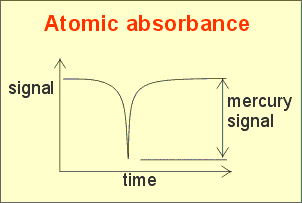 |
Concentration of mercury (c) is proportional to absorbance (A) of the gas flowing thtough the
optical cell:
The factor k is dependent on
length of the optical cell, wavelength of the light and properties of
atoms absorbing this light. The absorbance A is defined by the following
equation:
where: I0 -
intensity of the light before absorption and I - after absorption.
|
As the UV-lamps are used
electrodeless discharge low pressure mercury lamps (EDL). They generate
light at analytical wavelength 253.7 nm corelated with maximum
absorbance of mercury vapor. The EDL lamps have long lifetime, 20,000
hours. Mercury vapours in these lamps are excited by high-frequency
electromagnetic waves.
The analytical signal from
the instrument is stabilized by several ways:
 EDL lamp
controller stibilizes the
light stream by measuring intensity of lamp light using beam splitter EDL lamp
controller stibilizes the
light stream by measuring intensity of lamp light using beam splitter
 absorbance
is independent on
intensity of light but on relation of entered and transmitted light absorbance
is independent on
intensity of light but on relation of entered and transmitted light
 the optical
cell is heated to ca.
70 oC the optical
cell is heated to ca.
70 oC
|

|



