Membrane formation process
This page presents membrane
capacitance during formation process.
Record
of capacitance was start directly after place of drop of forming
solution
into the hole. In the first stage the capacitance is low, the membrane
is thick (several micrometers). Next stage is visible as a fast
increase of
capacitance
- a bilayer is established and their area inreases. Last stage is
further
slow increase of capacitance. After a time the capacitance is stable -
the membrane is ready for experiments. The results were obtained using
the KSP
measurement system with the software for recording membrane
capacitance.
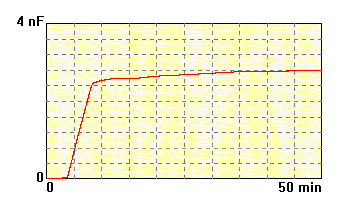 |
The membrane made of
lecithin and cholesterol 7:3 dissolved
in n-decane
(20 mg/ml), electrolyte 0.1M KCl. The formation process is right and
obtained
membrane is stable. |
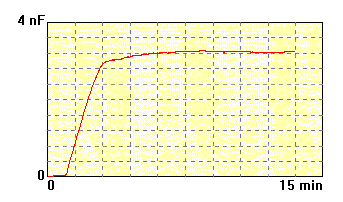 |
The membrane made of
lecithin and cholesterol 3:2 dissolved
in n-decane
(20 mg/ml), electrolyte 0.1M KCl. This membrane was formed much faster
than previous one. |
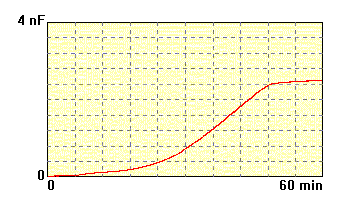 |
The membrane made of
lecithin dissolved in n-decane,
concentration
20 mg/ml, electrolyte 0.1M KCl. Time of formation of this membrane is
much
long. Shorter time is more desirable. |
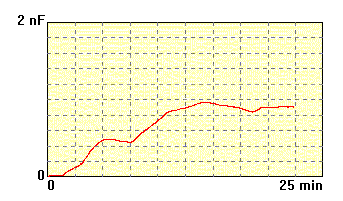 |
The membrane made of
lecithin dissolved in n-decane,
concentration
20 mg/ml, electrolyte 0.1M KCl. The process of membrane formation is
not
stable and membrane has low and not stable capacitance. The bilayer
occupies
small part of the hole, Plateau-Gibbs border is large. This membrane is
not useful for further experiments. |
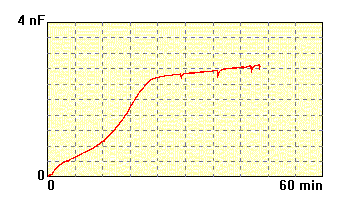 |
The membrane made of
mixture of phosphatidylcholine,
phosphatidylethanolamine,
and cholesterol 3:1:1 dissolved in n-decane, lipid concentration 20
mg/ml,
electrolyte: 0.1M KCl, 10mM HEPES, pH 7.0. This membrane has long time
of formation and is not stable. |
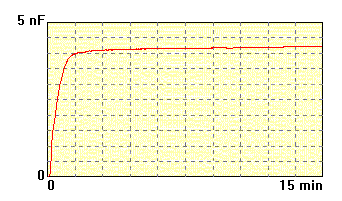 |
The mambrane made of
phosphatidylcholine and suspension of
steroid
dimer, 20 mg/ml, electrolyte 0.1M KCl. The formation process is fast
and
obtained membrane is stable. |
|