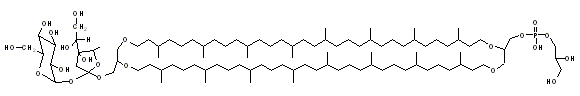
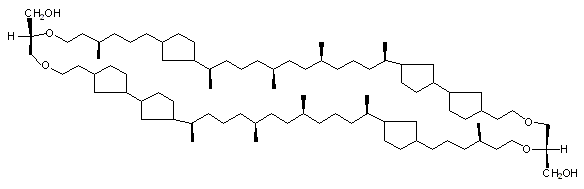
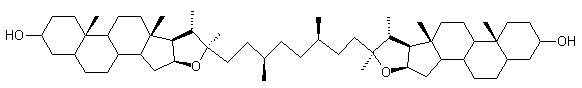
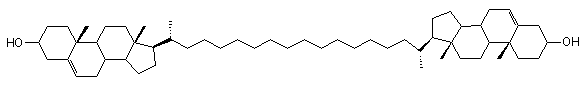Bolaamphiphilic
steroid dimers

|
Last modified: January 1, 2006
|
Microorganisms living in very
difficult environment like hot water of geysers or acidic waters have a
special kind of lipids in their cell membranes. The lipids have
bolaamphiphilic structure [1-7]. Their length is equal to the membrane
thickness. The lipids "span" the monolayers of the membranes increasing
their resistance on the environment. Examples of these lipid are shown
on following figures:
Cholesterol have a spatial structure regulating physico-chemical
properties of the cell membranes e.g. fluidity, resistance. The
properties of two kind of lipids - bolaamphiphilic and sterols were a
reason of synthesis bolaamphiphilic steroid dimers with length fitted
to the membrane thickness.
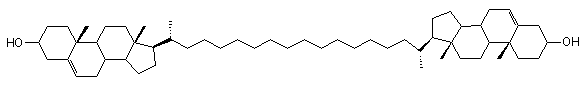
Bilayer lipid membranes formed from phosphatidylcholine with addition
of the dimers have following properties [9]:
- The process of spontaneous formation of the membranes by
the Mueller-Rudin method is much faster and the membranes are more
stable like without the dimers.
- The thickness of the membranes is lower what is caused by
smaller amount of the solvent remained between the monolayers.
- The membranes have higher voltage of breakdown.
- The membrane thickness is less susceptible on changes
caused by membrane potential (lower electrocompressibility).
References
- Fan
Q., Relini A., Cassinadri D., Gambacorta A., Gliozzi A., Stability
against temperature and external agents of vesicles composed of
archaeal
bolaform lipids and egg PC, Biochim.
Biophys. Acta, 1240 (1995) 83-88.
- Gambacorta
A., Gliozzi A., De Rosa M., Archaeal lipids and their biotechnological
applications, World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 11
(1995) 115-131.
- Gliozzi
A., Relini A. Lipid vesicles as model systems for Archaea membranes,
Ed.
Barenholz Y., Lasic D.D., Handbook of nonmedical applications of
liposomes,
vol. II, CRC Press, Boca Raton 1996, 329-348.
- Gliozzi
A., Relini A., Chong P.L.G., Structure and permeability properties of
biomimetic membranes of bolaform archaeal tetraether lipids, J.
Membrane
Sci., 206 (2002) 131-147.
- Gliozzi
A., Relini A., Rolandi R., Dante S., Gambacorta A., Organization of
bipolar lipids in monolayers at the air-water interface, Thin Solid
Films,
242 (1994) 208-212.
- Moss
R.A., Li J.M., Bilayer-bridging bolaamphiphilic lipids, J. Am.
Chem.
Soc., 114 (1992) 9227-9229.
- Stern
J., Freisleben H.J., Janku S., Ring K., Black lipid membranes of
tetraether lipids from Thermoplasma acidophilum, Biochim.
Biophys.
Acta, 1128 (1992) 227-236.
- Morzycki J, Kalinowski S., Lotowski Z., Rabiczko J.,
Synthesis
of dimeric steroids as components of lipid membranes, Tetrahedron, 53
(1997) 10579-10590.
- Kalinowski S., Łotowski Z., Morzycki J.W., Influence of
bolaamphiphilic steroid dimer on formation and structure of bilayer
lipid membranes, Cell. Molec. Biol.
Lett., 5 (2000) 107-128.
|